Introduction
In the realm of dentistry, achieving precision and patient comfort is vital for successful diagnostic imaging and treatment procedures. Bite Blocks are indispensable tools designed to support patient stability, enhance imaging accuracy, and improve overall dental experiences. This guide explores the importance of bite blocks, the modern materials enhancing their functionality, and the key benefits they bring to dental practices.
The Role of Bite Blocks in Dentistry
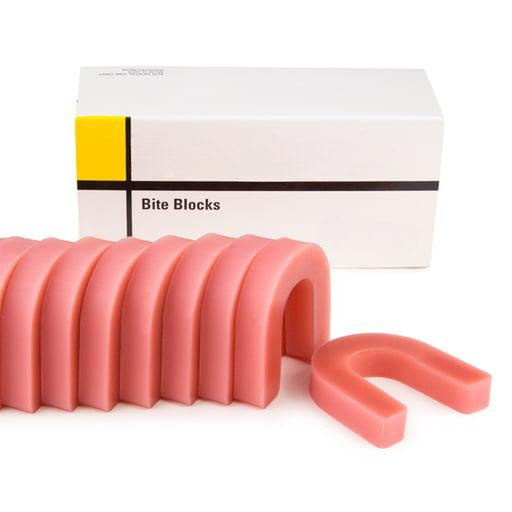
Bite blocks are positioning aids used in various dental procedures, from radiographic imaging to impression-taking and orthodontic treatments. They provide stability by maintaining the patient’s bite in a specific position, helping to capture clear images or secure molds with minimal discomfort. With advancements in materials, modern bite blocks offer better adaptability, hygiene, and comfort than ever before.
Modern Materials in Bite Block Design
Recent innovations in bite block materials have significantly improved their functionality and comfort. The materials most commonly used today include:
- Medical-Grade Silicone
- Features: Soft, flexible, and hypoallergenic, medical-grade silicone adapts well to the contours of the mouth, providing a comfortable fit.
- Benefits: Reduces discomfort and minimizes the risk of irritation, especially during longer procedures.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
- Features: Durable yet pliable, TPE is an ideal choice for bite blocks requiring a secure hold without causing excessive pressure.
- Benefits: Offers a comfortable, snug fit and can be easily sterilized, making it a hygienic option.
- Polyethylene Foam
- Features: Lightweight and gentle, polyethylene foam is frequently used in disposable bite blocks, offering cushioning for single-use applications.
- Benefits: Ensures patient comfort and reduces the need for sterilization, making it convenient for practices with high patient turnover.
- Non-Latex Rubber
- Features: Safe for patients with latex allergies, non-latex rubber is flexible and resilient.
- Benefits: Provides a firm grip without risk of allergic reactions, suitable for sensitive patients.
Key Specifications of Modern Bite Blocks
- Size and Shape Variability
- Options: Bite blocks come in various sizes and shapes, accommodating different age groups and dental arch sizes. Pediatric, standard adult, and large sizes are often available.
- Advantage: Ensures accurate placement for diverse patient needs, from children to adults.
- Sterilizable and Disposable Options
- Sterilizable Bite Blocks: Designed for multiple uses, sterilizable bite blocks are often made from medical-grade materials that withstand autoclaving.
- Disposable Bite Blocks: Crafted for single use, disposable options reduce cross-contamination risk and save on sterilization time.
- Ergonomic Design
- Modern bite blocks feature contoured edges and smooth surfaces to prevent soft tissue damage.
- Advantage: Enhances patient comfort and prevents slippage during procedures.
- Color-Coding
- Many bite blocks are color-coded to differentiate sizes or designated uses, making them easily identifiable during procedures.
- Benefit: Speeds up selection and organization, optimizing workflow in the dental practice.
Benefits of Using Modern Bite Blocks in Dental Procedures
- Improved Imaging Accuracy: Bite blocks stabilize the patient’s jaw, ensuring a steady position that enhances the accuracy of radiographic and 3D imaging.
- Increased Patient Comfort: Soft and flexible materials conform to the patient’s bite, minimizing discomfort and anxiety during extended procedures.
- Enhanced Infection Control: Disposable bite blocks or sterilizable materials uphold hygiene standards, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
- Efficient Workflow: Color-coded and ergonomic designs make it easier for practitioners to select, position, and maintain bite blocks, improving procedural efficiency.
Applications of Bite Blocks in Dentistry
- Radiographic Imaging
- Bite blocks help stabilize the patient’s head and jaw for intraoral X-rays, panoramic imaging, and CBCT scans, leading to clear and consistent images.
- Impression Taking
- Bite blocks secure the dental arch in a steady position, enabling accurate impressions, which are critical for creating well-fitting crowns, bridges, and orthodontic appliances.
- Orthodontic Procedures
- During orthodontic treatments, bite blocks aid in the precise placement of brackets and wires, ensuring effective alignment and patient comfort.
- Surgical Procedures
- Bite blocks are used to maintain the mouth’s open position in a relaxed manner during certain surgical procedures, helping to prevent jaw fatigue.
Best Practices for Using Bite Blocks
- Select the Appropriate Size: Choose a size that best fits the patient’s dental arch to prevent unnecessary pressure or movement.
- Sterilize or Dispose as Needed: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for sterilizable or disposable bite blocks to maintain hygiene.
- Monitor Patient Comfort: Regularly check with patients during procedures, adjusting as needed to ensure comfort without compromising positioning.
- Use Correct Placement Techniques: Proper placement is essential for bite blocks to function effectively without interfering with the procedure.
Conclusion
Bite blocks are essential tools that significantly impact both the accuracy of dental procedures and the comfort of patients. Advances in materials, such as medical-grade silicone and TPE, have made modern bite blocks more adaptable, hygienic, and comfortable. By choosing high-quality bite blocks and adhering to best practices, dental professionals can enhance both procedural precision and patient satisfaction, setting the standard for excellence in dental care.
FAQ: Enhancing Dental Precision and Comfort with Modern Materials Bite Blocks
1. What are bite blocks, and why are they used in dental procedures?
Bite blocks are positioning aids that help stabilize a patient’s bite during dental procedures, such as imaging, impression-taking, orthodontic adjustments, and some surgeries. They ensure accurate positioning, reduce patient movement, and enhance comfort throughout the procedure.
2. What materials are commonly used in modern bite blocks?
Modern bite blocks are made from materials such as medical-grade silicone, thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), polyethylene foam, and non-latex rubber. These materials offer durability, flexibility, comfort, and hypoallergenic properties, which are essential for patient safety and comfort.
3. Are there different sizes of bite blocks available?
Yes, bite blocks come in various sizes, including pediatric, standard adult, and larger sizes, to accommodate different age groups and dental arch sizes. This ensures each patient has a secure, comfortable fit that supports accurate positioning.
4. Are bite blocks reusable or disposable?
Bite blocks are available in both sterilizable (reusable) and disposable options. Sterilizable bite blocks are designed for multiple uses and can withstand autoclaving, while disposable ones are intended for single-use to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
5. How do bite blocks improve imaging accuracy?
Bite blocks help keep the patient’s jaw steady during radiographic imaging, preventing movement that could blur images. This stability enhances the accuracy of X-rays, CBCT scans, and 3D imaging, providing clear, precise visuals for diagnosis and treatment planning.
6. Can bite blocks be uncomfortable for patients?
Modern bite blocks are designed with patient comfort in mind. They are typically made from soft, flexible materials like medical-grade silicone or TPE, which adapt to the shape of the patient’s bite and reduce pressure on soft tissues. Their ergonomic design also minimizes discomfort during extended procedures.
7. What procedures benefit from the use of bite blocks?
Bite blocks are beneficial in a range of dental procedures, including:
- Radiographic imaging (e.g., intraoral X-rays, CBCT scans)
- Dental impression-taking for crowns, bridges, and other restorations
- Orthodontic treatments for bracket and wire placement
- Surgical procedures that require maintaining the mouth open comfortably
8. How should bite blocks be cleaned and sterilized?
Sterilizable bite blocks should be cleaned and autoclaved according to the manufacturer’s instructions after each use. Disposable bite blocks should be discarded after a single use to maintain hygiene and reduce contamination risk.
9. Are bite blocks suitable for patients with latex allergies?
Yes, many modern bite blocks are made from non-latex rubber or other hypoallergenic materials, ensuring safety for patients with latex allergies.
10. How do color-coded bite blocks help in dental practices?
Color-coded bite blocks help practitioners quickly identify the appropriate size or type for a procedure, improving efficiency and streamlining the workflow within the dental practice.
11. Can bite blocks be used for children?
Yes, bite blocks are available in pediatric sizes specifically designed to fit smaller dental arches comfortably and securely, making them suitable for children as well as adults.
12. Are bite blocks cost-effective for dental practices?
Yes, bite blocks can save time and costs in the long term by improving procedural accuracy, reducing the need for retakes or adjustments, and enhancing patient comfort. Both reusable and disposable options offer cost-effective solutions tailored to the needs of high-traffic dental practices.